Choose Language
March 5, 2021
FocusIs Crypto Becoming Mainstream? | Part II – An alternative form of money?
Is crypto becoming mainstream?
Welcome to the second article in our focus series on cryptocurrencies. Following our primer, that explained what cryptocurrencies are and how they work, we will now go on to explore if they could ever be considered as a viable alternative to money...
Part II
Cryptocurrency as an alternative form of money?
Historically, money has either had intrinsic value or derived value from government decree. Using money electronically generally has involved using the private ledgers and systems of at least one trusted intermediary. Cryptocurrencies, by contrast, generally employ user agreements, a network of users, and cryptographic protocols to achieve valid transfers of value. Cryptocurrency users typically use a pseudonymous address to identify each other and a passcode or private key to make changes to a public ledger to transfer value between accounts. Other computers in the network validate these transfers. Through this use of blockchain technology, cryptocurrency systems protect their public ledgers of accounts from manipulation, so that users can only send cryptocurrency to accounts which they have access to, thus allowing users to make valid transfers without a centralized, trusted intermediary.
Money serves three interrelated economic functions: it is a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. To function as a medium of exchange, it must be tradable and agreed to have value. To function as unit of account, it must act as a good measurement system. To function as a store of value, it must be able to purchase approximately the same value of goods and services at some future date as it can purchase now.
How well cryptocurrencies can serve those functions relative to existing money and payment systems will likely play a large part in determining cryptocurrencies’ future value and importance. The debate is very passionate, with crypto supporters saying that economists are dinosaurs and economists saying that crypto supporters are just selling a bubble.
Proponents of the technology argue cryptocurrency can effectively serve the economic functions of money. They contend that a decentralized system using cryptocurrencies will ultimately be more efficient and secure than existing monetary and payment systems.
Sceptics doubt that cryptocurrencies can effectively act as money and achieve widespread use. They note various obstacles to the extensive adoption of cryptocurrencies, including economic (e.g., existing trust in traditional systems and volatile cryptocurrency value), technological (e.g., scalability), and usability obstacles (e.g., access to equipment necessary to participate). In addition, sceptics assert that cryptocurrencies are currently overvalued and under-regulated.
Volatility
From a dispassionate angle, the volatility in the price of Bitcoin suggests it functions poorly as a unit of account and a store of value.
Bitcoin volatility (21-day rolling, annualized)
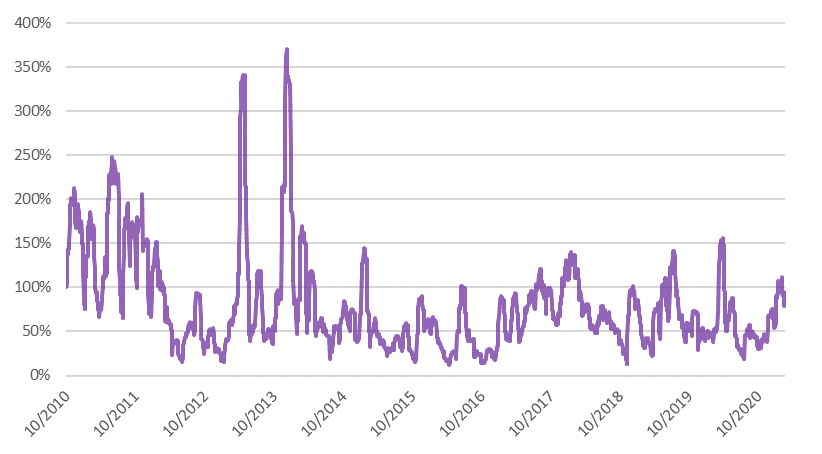

Source: Bloomberg, BIL
Compared to most investments, Bitcoin is a highly volatile, high-risk investment. If you look historically at the price of bitcoins, there have been several occasions where it spiked and then came crashing down quickly. While that can mean big returns, it can also mean big losses.
To the delight of investors and the financial media, the price of Bitcoin has been skyrocketing. But the question is also at what price and to which extent investors can navigate the nail-biting roller-coaster journey. This is the double-edged sword of investing in volatile assets: they can produce above-average returns, but often expose the investor to deep, frequent, and sometimes lethal drawdowns.
Standard deviation is the most common measure of volatility, but standard deviation reduces the investment down to a single number, which can be difficult to conceptualize.
Bitcoin’s maximum drawdowns, % (2010 – Feb 2021)
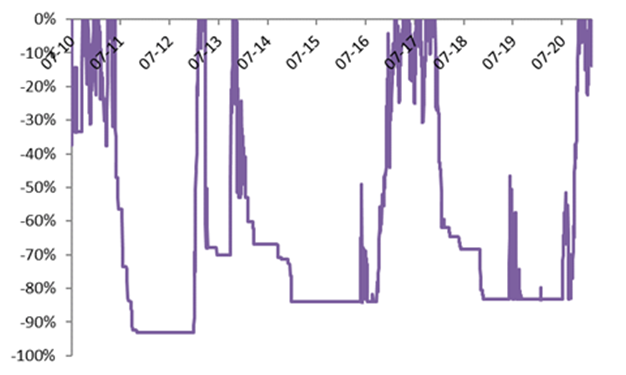

Source: Bloomberg, BIL
Historical drawdowns highlight the perspective of Russian roulette. With retail investors forming a crucial part of the Bitcoin trend, we must hope they are all well prepared to lose all their money on crypto investments. The adage that there is no return without risk is valid in every investment, but the problem with Russian roulette is that even if the bullet is made of silver, is that if you do not have luck, whatever your skills, there is no way back after the shot is fired.
Are we serious when discussing that cryptocurrencies could replace traditional currency? Just imagine the potential impact it could have on economic activity and monetary policy if it was ever to be considered as a real currency. As stated by P. Donovan (UBS Chief Economist), “It is worth noting that the crypto Bitcoin had a collapse in spending power that would constitute hyperinflation were it a proper currency”. With the idea that a currency needs to be a stable store of value, we do not believe that cryptos are currently eligible. For now, there is no guarantee that the basket of goods that you can buy with bitcoins today will be the same as the one you will be able to buy tomorrow.
Cryptocurrencies can have significant value fluctuations within short periods of time; as a result, pricing goods and services in units of cryptocurrency would require frequent repricing and likely would cause confusion among buyers and sellers. To be considered as a proper currency, a store of value that can achieve stable spending power, the balance of supply and demand needs to be maintained. With traditional currency, this is achieved by central banks, who can reduce or increase supply to maintain spending power. In the Bitcoin world, the embedded limited supply is not enough to maintain stable purchasing power. Having no certainty about what could be bought from one unit of bitcoin, nor about what could be stored when using Bitcoin as a savings vehicle, sounds more like gambling than investing.
Scalability
Worth to mention, Bitcoin also faces scalability problems. There is a limited rate at which the Bitcoin network can process transactions. This is related to the fact that blocks in the Bitcoin blockchain are limited in size and frequency. At least for now, bottlenecks in the Bitcoin transaction processing capacity are real. According to Statista, the number of bitcoins processed on a single day reached its highest value at the beginning of 2021, reaching around 400,000 daily transactions. This is a very small number in comparison to established electronic payment networks. [1]
Here again, the divide between proponents and sceptics is evident, with the first group asserting that cryptocurrencies’ potential benefits will be realized in the coming years or decades, leading to widespread adoption, while sceptics emphasize the obstacles facing the widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies and doubt that these challenges can be overcome.
Network Effects
Finally, currencies are also subject to network effects, wherein their value and usefulness depends in part on how many people are willing to use them. Currently, a relatively small number of businesses or individuals use or accept cryptocurrencies as payment. Unlike the dollar and most other government-backed currencies, cryptocurrencies are not legal tender, meaning creditors are not legally required to accept them to settle debts or to pay taxes.
The truth is that money is just a construction. Some sort of Matrix (the movie) blue pill. All that is required for a form of money to hold value is trust and adoption. In the case of Bitcoin, this can be measured by its growing base of users, merchants, and start-ups. As with all currency, Bitcoin's value comes only and directly from people willing to accept them as payment.
Disintermediation
The idea of disintermediation is nevertheless not as simple as crypto fans want to present it. In general, when a buyer of a good or a service provided remotely sends a cryptocurrency to another account, that transaction is irreversible and made to a pseudonymous identity. Although a cryptocurrency platform validates that the currency has been transferred, the platform generally does not validate that a good or service has been delivered. Unless a transfer is done face-to-face, it will involve some degree of trust between one party and the other or a trusted intermediary. These risks could act as a disincentive to parties considering using cryptocurrencies in certain transactions and thus could hinder cryptocurrencies’ ability to act as a medium of exchange. Sending cash to someone in another location presents a similar problem, which historically has been solved by using a trusted intermediary.
In response to this problem, several companies offer cryptocurrency escrow services. Typically, the escrow company holds the buyer’s cryptocurrency until delivery is confirmed. Only then will the escrow company pass the cryptocurrency onto the seller. Although an escrow service may enable parties who otherwise do not trust each other to exchange cryptocurrency for goods and services, the use of such services reintroduces the need for a trusted third-party intermediary in cryptocurrency transactions, an escrow company that will not abscond with the cryptocurrency while adequately protected against hacking. If cryptocurrencies ultimately require their own system of intermediaries to function as money, questions may arise about whether this requirement defeats their original purpose.
Don't miss the next article in the series which will take a look at cryptocurrencies from a portfolio management standpoint.
Footnotes:
- Visa’s payment systems processed on average 379 million transactions per day (source: Visa annual report 2019)
Disclaimer
All financial data and/or economic information released by this Publication (the “Publication”); (the “Data” or the “Financial data
and/or economic information”), are provided for information purposes only,
without warranty of any kind, including without limitation the warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular
purpose or warranties and non-infringement of any patent, intellectual property or proprietary rights of any party, and
are not intended for trading purposes. Banque Internationale à Luxembourg SA (the “Bank”) does not guarantee expressly or
impliedly, the sequence, accuracy, adequacy, legality, completeness, reliability, usefulness or timeless of any Data.
All Financial data and/or economic information provided may be delayed or may contain errors or be incomplete.
This disclaimer applies to both isolated and aggregate uses of the Data. All Data is provided on an “as is” basis. None of
the Financial data and/or economic information contained on this Publication constitutes a solicitation, offer, opinion, or
recommendation, a guarantee of results, nor a solicitation by the Bank of an offer to buy or sell any security, products and
services mentioned into it or to make investments. Moreover, none of the Financial data and/or economic information contained on
this Publication provides legal, tax accounting, financial or investment advice or services regarding the profitability or
suitability of any security or investment. This Publication has not been prepared with the aim to take an investor’s particular investment objectives,
financial position or needs into account. It is up to the investor himself to consider whether the Data contained herein this
Publication is appropriate to his needs, financial position and objectives or to seek professional independent advice before making
an investment decision based upon the Data. No investment decision whatsoever may result from solely reading this document. In order
to read and understand the Financial data and/or economic information included in this document, you will need to have knowledge and
experience of financial markets. If this is not the case, please contact your relationship manager. This Publication is prepared by
the Bank and is based on data available to the public and upon information from sources believed to be reliable and accurate, taken from
stock exchanges and third parties. The Bank, including its parent,- subsidiary or affiliate entities, agents, directors, officers,
employees, representatives or suppliers, shall not, directly or indirectly, be liable, in any way, for any: inaccuracies or errors
in or omissions from the Financial data and/or economic information, including but not limited to financial data regardless of the
cause of such or for any investment decision made, action taken, or action not taken of whatever nature in reliance upon any Data
provided herein, nor for any loss or damage, direct or indirect, special or consequential, arising from any use of this Publication
or of its content. This Publication is only valid at the moment of its editing, unless otherwise specified. All Financial data and/or
economic information contained herein can also quickly become out-of- date. All Data is subject to change without notice and may not be
incorporated in any new version of this Publication. The Bank has no obligation to update this Publication upon the availability of new data,
the occurrence of new events and/or other evolutions. Before making an investment decision, the investor must read carefully the terms and
conditions of the documentation relating to the specific products or services. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance.
Products or services described in this Publication may not be available in all countries and may be subject to restrictions in some persons
or in some countries. No part of this Publication may be reproduced, distributed, modified, linked to or used for any public or commercial
purpose without the prior written consent of the Bank. In any case, all Financial data and/or economic information provided on this Publication
are not intended for use by, or distribution to, any person or entity in any jurisdiction or country where such use or distribution would be
contrary to law and/or regulation. If you have obtained this Publication from a source other than the Bank website, be aware that electronic
documentation can be altered subsequent to original distribution.
As economic conditions are subject to change, the information and opinions presented in this outlook are current only as of the date
indicated in the matrix or the publication date. This publication is based on data available to the public and upon information that is
considered as reliable. Even if particular attention has been paid to its content, no guarantee, warranty or representation is given to the
accuracy or completeness thereof. Banque Internationale à Luxembourg cannot be held liable or responsible with respect to the information
expressed herein. This document has been prepared only for information purposes and does not constitute an offer or invitation to make investments.
It is up to investors themselves to consider whether the information contained herein is appropriate to their needs and objectives or to seek advice
before making an investment decision based upon this information. Banque Internationale à Luxembourg accepts no liability whatsoever for any investment
decisions of whatever nature by the user of this publication, which are in any way based on this publication, nor for any loss or damage arising
from any use of this publication or its content. This publication, prepared by Banque Internationale à Luxembourg (BIL), may not be copied or
duplicated in any form whatsoever or redistributed without the prior written consent of BIL 69, route d’Esch ı L-2953 Luxembourg ı
RCS Luxembourg B-6307 ı Tel. +352 4590 6699 ı www.bil.com.
Read more
More
December 9, 2024
Weekly InsightsWeekly Investment Insights
December is here, and while the cold, dark days may not be everyone's cup of cocoa, the festive spirit is starting to set in....
December 2, 2024
Weekly InsightsWeekly Investment Insights
In an age where you can carry a computer, music player, phone, TV, camera, calculator and notebook all in one small device that fits...
November 25, 2024
Weekly InsightsWeekly Investment Insights
After last week's disappointing Eurozone economic data, another ECB rate cut in December is high on the wish list for Europe, with investors increasing...
November 22, 2024
BILBoardBILBoard December 2024 – Red Sweep
At BIL, we are long-term investors guided by stable, strategic asset allocation guidelines. However, our investment strategy itself is a living, breathing thing,...
November 18, 2024
Weekly InsightsWeekly Investment Insights
Less than two weeks after the US Presidential election, Trump has made significant progress in nominations for top government posts, leading to some market...

